+91-9958 726825
Impact Of AI In Algorithmic Trading Strategies A Comparative Analysis
|
Algorithmic trading has been revolutionising financial markets by using the advanced technology, such as the artificial intelligence (AI), to make the trading decisions. In this paper, a comprehensive comparative analysis was made about the impact of AI in algorithmic trading strategy. Firstly, we trace the journey of algorithmic trading and stress on the use of AL in enriching the trading strategies. Traditionally, algorithmic trading strategies are compared with the AI – based strategies and all the pros and cons in using them are highlighted. In addition, our case studies and empirical evidence attempt to ascertain the track and effectiveness of performance of an AI in algorithmic trading. However, our analysis indicates that AI has already extended the capabilities of AI – by providing more efficient decision making, improved accuracy and risk management, to name a few. Though these advances have been made, issues like the quality of data, and the ability to interpret the model, as well as compliance with regulations still exist. The implications of these findings for practitioners and researchers are discussed in the paper to show how AI can be properly used in financial markets.
|
|
Algorithmic trading or algo trading is the business of trading various financial instruments such as equities, currencies, commodities or other derivatives using computer algorithms with a view to making a profit. The advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques has made it easier and possible to analyse a large amount of dataset and make sense of the data for smarter trading algorithms. This paper performs a thorough investigation on the effect of AI in algorithmic trading strategies, contrasting traditional strategies and AI based strategies and discusses the pros and cons of each.
For financial markets, algorithmic trading has revolutionised the trading world as traders are able to trade at speeds and frequencies that were never thought possible. Furthermore, there is a big influence of the advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies that allowed the trading algorithms to analyse large data sets and make multiple decisions in an instant. |
|
Review the Evolution of Algorithmic Trading: The study intends to give a detailed review of the evolution of algorithmic trading; this is with the aim of identifying key milestones as well as developments that have contributed to the formation of the industry.
Assess the Role of AI in Algorithmic Trading: The study attempts to evaluate the role of Artificial Intelligence in Algorithmic Trading strategies by comparing traditional approaches with the ones based on Artificial Intelligence. Compare Traditional vs. AI-Based Strategies: A comparison will be done to compare the performance as well as efficiency and adaptability of traditional algorithmic trading strategies vs. the ones based on AI. Identify Challenges and Limitations: The study tries to Identify and Analysis of challenges and limitations that can be associated with use of AI for algorithmic trading like issues in data quality, model interpretability, and regulatory issues etc. Provide Insights for Practitioners and Researchers: The study aims to give insights and recommendations for practitioners and researchers working on the algorithmic trading field and discussing the best practice and areas that need to be studied further. Contribute to the Understanding of AI in Algorithmic Trading: By addressing these objectives, the study aims to contribute to the broader understanding of the role of AI in algorithmic trading and its implications for financial markets. Role of AI in algorithmic trading strategies Data Analysis: AI Algorithms: AI algorithms are capable of analyzing vast amounts of data, varying from market prices to news articles about the market, the sentiment in the social media and the economic indicators, to figure out a trade, they could potentially indicate. Since this is data driven, the algorithms can make better and more timely decisions. Pattern Recognition: AI algorithms are great at identifying complex pattern in the data that human traders may fail to spot. AI powered algorithms are able to predict the future market movement with very high probability when they recoganise these patterns. Adaptability: Additionally, adaptability is one of the strengths of AI in algorithmic trading since it can adapt to changing conditions of the market. Traditionally however, machine learning algorithms don’t provide enough flexibility as they have a limited number of hypotheses – that is, they can only test a certain set of assumptions and the input data fed into the algorithms is very rigid. Risk Management: AI algorithms can also be used in risk management in algorithmic trading. AI algorithms analyse historical data and market trend to detect the risk in time so as to take proactive measures such as adjusting position size or placing stop loss orders. Speed and Efficiency: AI-Based trading systems improve Speed and Efficiency; they can carry out operations much more rapidly than a human operator. The advantage of speed afforded by AI algorithms enables them to trade on and realize fleeting market opportunities and achieve near to minimum trade latency. Reduced Human Bias: AI algorithms are not emotions, nor are they biased, both of which can influence trading decisions. With the removal of these biases, the AI powered algorithms can take a rational and objective trading decision.
Table 1 : Comparative Analysis of Traditional vs. AI-Based Strategies
Limitations of AI in Algorithmic Trading
Data Dependence: The quality of AI systems depends on the quality of the data they process. When phony or automated tweets skewed market signals in 2018, certain hedge funds that depended on sentiment analysis on Twitter experienced losses. In a similar vein, AI systems have produced deceptive buy/sell signals as a result of delayed or erroneous economic data releases, increasing losses rather than decreasing them. Complexity and Interpretability: Deep learning in particular is one of the many AI models that function as "black boxes." The decision-making process is sometimes incomprehensible to traders and regulators. This lack of openness erodes confidence and creates legal issues. For instance, algorithms accelerated a sharp decline in the market during the 2010 Flash Crash, but authorities found it difficult to assess the impact of AI-driven tactics because of their low interpretability. Computational Resources: Cloud infrastructure, high-performance hardware, and frequent updates are necessary to run complex AI models. Market concentration results from the exclusion of smaller businesses lacking these resources. The competitive gap is widened by the fact that most boutique enterprises are unable to match the extensive computing infrastructure used to construct JP Morgan's LOXM AI trading system. Market Dynamics: In uncommon or unheard-of situations, AI models frequently fail. Many AI funds educated on "normal" conditions were unable to forecast high volatility during the COVID-19 market meltdown in March 2020, which led to enormous sell-offs and exacerbated the decline. In a similar vein, unanticipated geopolitical shocks (such as Russia's invasion of Ukraine in 2022) demonstrated that AI models frequently have trouble identifying non-financial risk variables.
Ethical Considerations: Systems powered by AI may inadvertently raise systemic risk. Bond markets in 2019 saw abrupt liquidity shortages as a result of multiple hedge funds' simultaneous AI-driven momentum strategies. Fairness is another ethical issue that comes up as institutional investors that use AI outperform individual traders, casting doubt on the equality of access in the financial markets.
Overfitting and Generalization: AI models frequently perform poorly in real time but well on historical data. Due in large part to their models being over-fit to historical circumstances and unable to adjust to new realities, a number of AI-focused hedge funds that were introduced between 2016 and 2019 (such as Sentient Technologies) under-performed following rigorous backtests. |
|
The impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on algorithmic trading techniques is investigated in this paper using a comparative and analytical methodology. To guarantee a thorough grasp of the topic, both primary and secondary data sources were consulted. Secondary data that gave background information on the development of algorithmic trading, the uptake of AI techniques, and the regulatory frameworks influencing their use in international markets was gathered from peer-reviewed publications, industry reports, whitepapers, and regulatory documents.
To gather the opinions of academics and practitioners, a structured survey was carried out in addition to secondary sources. Forty-two people participated in the study, including postgraduate finance students, financial analysts, and professional traders. It was sent online and had both closed-ended and open-ended questions intended to gauge knowledge of artificial intelligence (AI) in trading, opinions about its benefits over conventional approaches, and worries about its drawbacks, legal compliance, and moral dilemmas. While qualitative feedback was thematically coded to highlight common perspectives and issues, quantitative data was evaluated using descriptive statistics to identify patterns. This procedure yielded empirical data to support the conclusions gleaned from the literature. The report also includes a case study of the Knight Capital event in 2012 to highlight the practical ramifications of algorithmic and AI-driven trading. In this instance, a flaw in the company's automated trading system resulted in millions of incorrect trades in a matter of minutes, causing the company to lose $440 million in a single day and nearly go out of business. The example highlights the dangers of using intricate automated systems in financial markets without adequate testing and supervision, even though the system in question was not entirely AI-based. In the context of contemporary AI-driven systems, which are frequently harder to understand than conventional algorithms, the incident highlights how a lack of transparency and insufficient protections can have disastrous financial repercussions. This methodology offers both empirical and contextual depth by integrating a survey of current attitudes with literature research and a real-world case study. It addresses AI's drawbacks and the significance of regulatory supervision while enabling a fair evaluation of the technology's possible advantages in algorithmic trading. |
|
As big data grew and computing power increased in the early 2000s, the incorporation of AI into trading systems started to pick up steam [1] . Early research highlighted AI's capacity to handle enormous amounts of financial data, facilitating quick analysis and trade execution (Treleaven, Galas, & Lalchand, 2013). Artificial intelligence (AI) systems, especially those that use machine learning (ML), neural networks, and evolutionary algorithms, have the ability to recognize patterns in both historical and current data, which makes them more flexible than traditional quantitative models.
Predictive accuracy is one of AI's most important effects on algorithmic trading [1] . Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, a deep learning architecture, have been shown by Fischer and Krauss (2018) to significantly outperform conventional autoregressive models in stock price forecasting. Their analysis of the S&P 500 index showed that AI models could identify intricate non-linear patterns that traditional methods frequently miss. The durability of ensemble learning methods, such as random forests and gradient boosting, in surpassing logistic regression in financial forecasts was further confirmed by the study conducted by Krauss, Do, and Huck (2017) [6] . A branch of machine learning called reinforcement learning (RL) has drawn interest due to its capacity to discover the best trading strategies via trial and error [4]. A deep reinforcement learning framework for stock trading was created by Deng et al. (2016)[1] and it dynamically modified portfolio positions in reaction to shifting market conditions. Their model outperformed fixed-rule systems in terms of returns and volatility. This transition from static, tried-and-true methods to dynamic, real-time learning models highlights AI's primary benefit: its ability to adapt and improve over time. A study comparing the performance of AI-based trading algorithms to conventional moving average and momentum methods was carried out by Chan and Lo (2020). According to their research, AI-driven tactics produced better Sharpe ratios and were more shock-resistant. Conventional approaches were more vulnerable to erroneous signals during volatile times, although being simpler to understand and apply. The authors came to the conclusion that AI's higher performance was mostly due to its capacity to synthesis a variety of data sources, including unstructured text and historical prices[1] . Another revolutionary tool in AI's toolbox is Natural Language Processing (NLP). Bollen, Mao, and Zeng (2011) demonstrated how sentiment analysis using Twitter feeds could predict market movements with significant accuracy, and their study was a turning point in the use of unstructured data in trading strategies. More recent research has expanded on this innovation by using news analytics, earnings call transcripts, and even geopolitical developments as inputs for algorithmic models[1] . Even with its obvious benefits, AI in trading has drawbacks. The problem of overfitting in AI models, especially in deep learning applications, was brought to light by Zhang et al. (2021). In actual trading scenarios, models based on historical data could perform poorly since they don't generalize well to future market conditions [16] . Furthermore, interpretability and regulatory compliance are hampered by the "black-box" nature of many AI systems. According to the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO, 2018) [6] , stakeholders and regulators find it challenging to comprehend and oversee AI models' decision-making processes because to their opacity. Systemic and ethical issues are another area of concern [9] . As demonstrated by the 2010 Flash Crash, AI systems running at high frequencies can cause flash crashes and market instability. Explainable AI (XAI) should be used in trading algorithms to improve accountability and transparency, according to studies like those of Leinweber (2022) [12] . A recurrent subject in recent research is the necessity of strong governance mechanisms to oversee AI-based trading. Kroll, Barocas, and Felten (2017) state that integrating rule-based logic with machine learning enables the creation of strategies that are both interpretable and adaptive, and that hybrid models that combine AI with traditional statistical techniques are increasingly being proposed to mitigate some of these challenges [11] . This hybrid approach is becoming more and more popular in institutional trading environments where risk management and auditability are crucial. The use of artificial intelligence in algorithmic trading is reviewed by Hao and Chen[6] , who highlight how machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing enhance predicted accuracy and flexibility. To guarantee dependability in financial markets, they also draw attention to issues like overfitting, interpretability, and regulatory concerns, advocating for hybrid models and explainable AI. In their analysis of algorithmic trading in African markets, Baba-Yara, John, and Melecky (2020) conclude that although it improves efficiency and liquidity, it also increases the risk of instability, especially in less developed financial systems[1] . Guntuka (2024) talks about how algorithmic trading methods driven by AI are changing financial markets, emphasizing advancements in automation and predictive modeling that speed up and enhance decision-making[13] . Marimuthu (2025) examines AI-powered trading in foreign exchange markets, highlighting how technology can increase liquidity and efficiency while also raising concerns about possible volatility amplification[13] . The impact of algorithmic trading on investor portfolios is examined by Gopakumar, Dananjayan, and Narayanasamy (2023), who highlight both the potential for higher returns and the worries about elevated systemic risks[6] . |
|
|
According to the study, the majority of participants are aware of artificial intelligence's function in financial trading, demonstrating the technology's increasing significance in the sector. The technical difficulty of AI in this industry and the need for additional education is highlighted by the fact that many people only have a limited or moderate comprehension.
The lack of real-world experience with AI-based trading systems indicates that adoption is still slow. Nevertheless, most people think AI tactics are better than conventional approaches because of AI's speedy processing of big data sets and capacity to spot intricate patterns. However, some respondents are still unsure, perhaps as a result of worries about legislation, model transparency, or data quality. All things considered, even if AI's promise is acknowledged, issues with knowledge, application, and trust still need to be resolved for wider acceptance. |
Table 2 : Response of AI used in financial trading
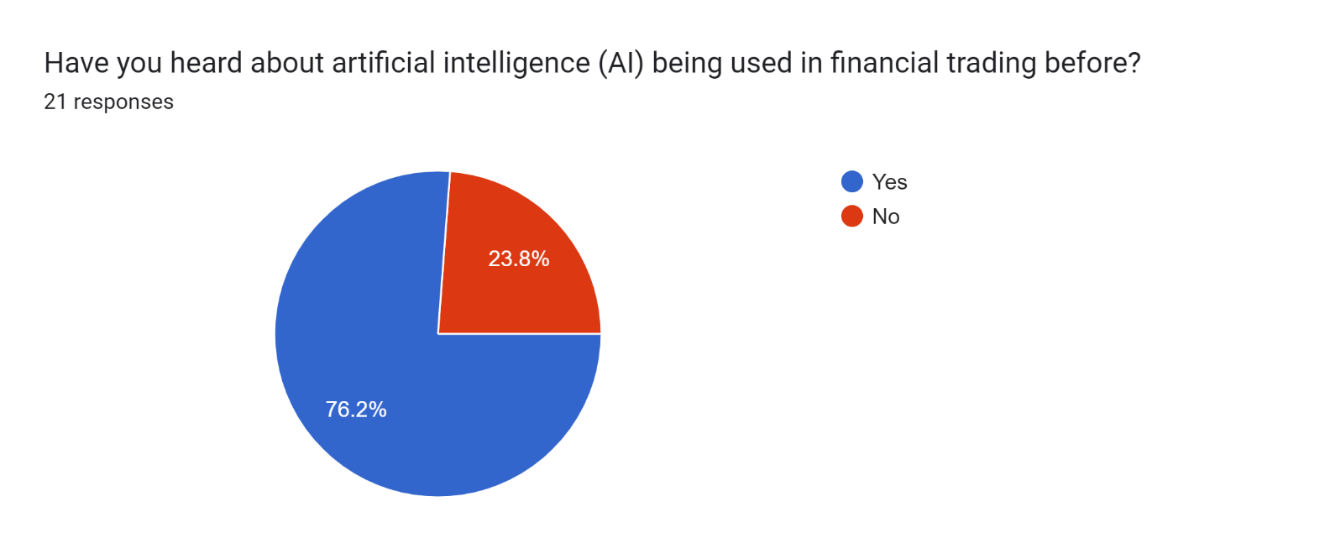 Pie Chart 1 : Graphical representation of Response of AI used in financial trading Interpretation: Financial trading is one of the things that AI is widely used in. If you look at statistics, 76.2 % YES is an undeniable proof of the fact that people know very well how AI can be used in this field. The use of AI in trading is to apply algorithmic trading, quantitative analysis, risk management and fraud detection. AI can analyse huge amounts of data, identify the patterns and make decisions much faster than humans could achieve, which makes it a very useful tool in fast-paced, data driven world of financial market.
Table 3 : AI Trending
Table 4 : AI Trending in Percentage
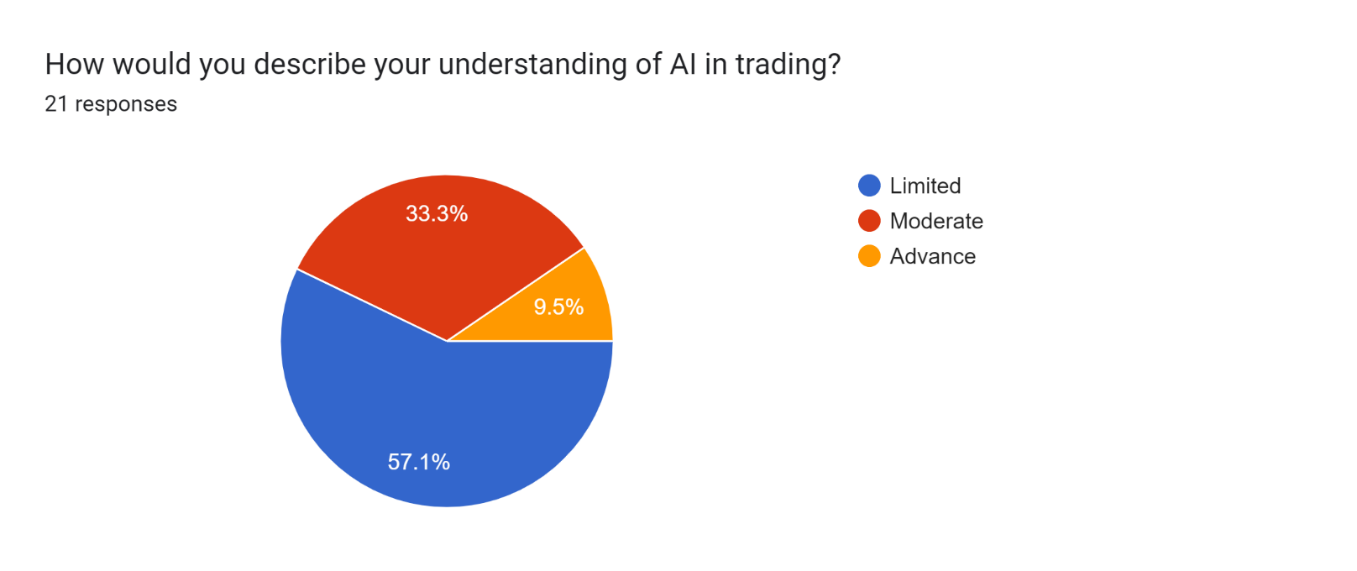 Pie Chart 2 : Graphical Representation of AI Trending
Interpretation: The answers indicate that the levels of understanding of the respondents concerning AI in trading is varied. The majority of respondents do not feel that they have an extensive understanding of this topic, even if moderate to limited. The fact that not many respondents think they have an advanced understanding of the subject matter indicates that AI in trading is a relatively complicated and niche subject that is not easy to understand for an average person. These responses in general demonstrate the significance of ongoing learning and development in the area of AI in trading.
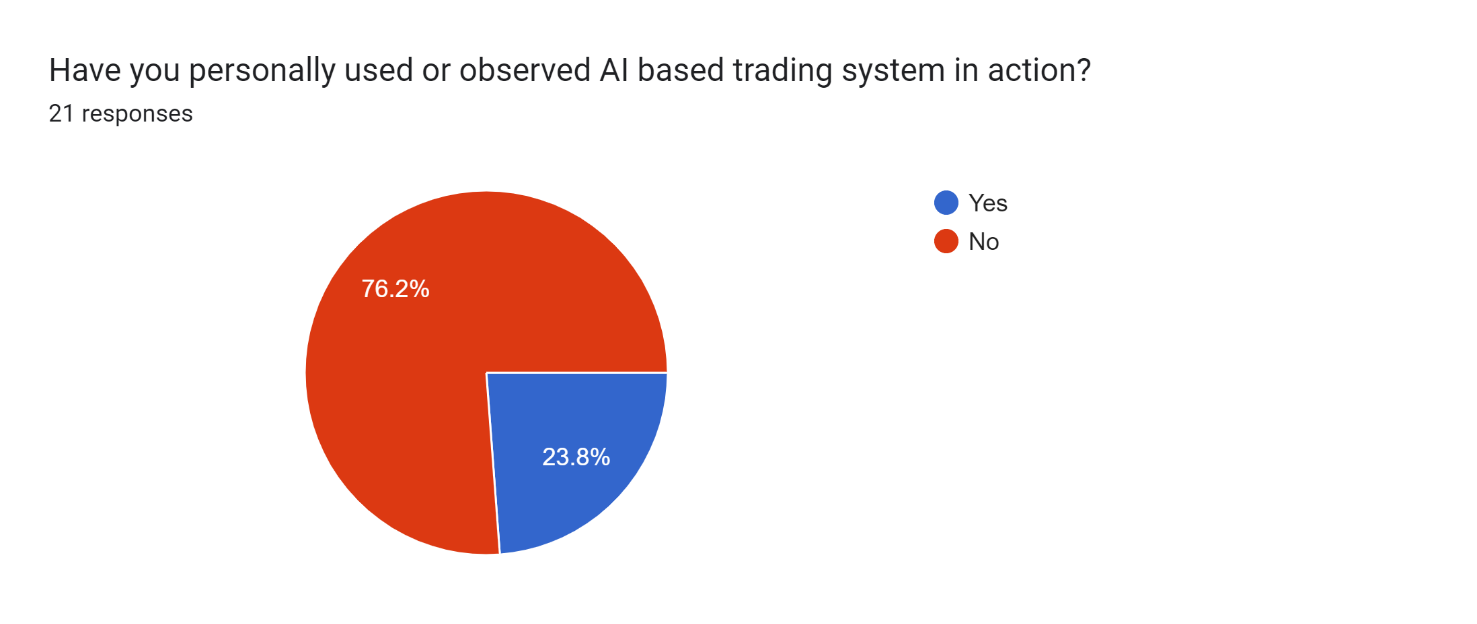 Pie Chart 3 : Graphical Representation of AI Based Trending System Interpretation: From the responses, 76.2% of the participants have not used or seen an AI based trading systems in action and 23.8% have used or seen AI based trading systems in action. However, this means that although some of the respondents have some level of direct experience with AI based trading systems, most respondents do not have exposure. This perhaps suggests a misalignment between theoretical knowledge or awareness of AI in trading and practise in terms of using or seeing such systems in real trading conditions.
Table 5 : AI based trading strategies
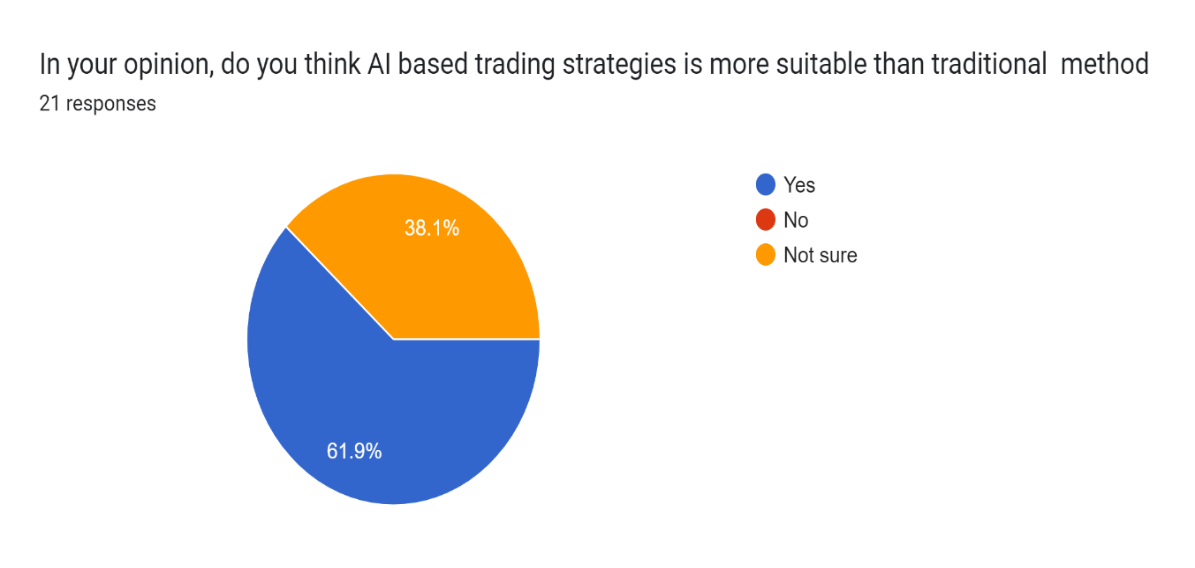 Pie Chart 4 : Graphical Representation of AI based trading strategies
Interpretation: According to the answers, 57.1% of participants think that AI based trading strategies are better than the traditional ones, 33.3% do not, and 9.5% have no idea. This shows that a lot of the respondents think that AI based trading strategies are better than the traditional ways of trading. The reasons for the increasing adoption of AI in trading can be due to advantages that AI offers which may include being able to process enormous data sets much faster and using complex patterns to make decisions and thus have the ability to make more informed and efficient trading decisions. The fact that not sure respondents could mean that they don’t have the information or experience with AI based trading strategies to come to a more definitive answer. |
|
This study contrasted algorithmic trading tactics driven by AI and traditional methods, demonstrating that while AI enhances data analysis, flexibility, and risk management, it also presents drawbacks such data dependence, interpretability issues, and regulatory problems. The Knight Capital case brought to light the dangers of inadequate monitoring in automated systems, while survey results indicated a considerable awareness of AI's potential despite its limited practical adoption.
Explainable AI, ethical protections, and hybrid models that strike a compromise between performance and transparency should be the main topics of future study. Algorithmic trading is being transformed by AI overall, but prudent governance and ongoing cooperation between researchers, practitioners, and regulators are essential to its long-term viability. |
|
|
 Pie Chart 1 : Graphical representation of Response of AI used in financial trading |
 Pie Chart 2 : Graphical Representation of AI Trending |
 Pie Chart 3 : Graphical Representation of AI Based Trending System |
 Pie Chart 4 : Graphical Representation of AI based trading strategies |
Dr. Manjusha Y. Patil (2025), Impact Of AI In Algorithmic Trading Strategies A Comparative Analysis. Samvakti Journal of Research in Information Technology, 6(2) .





